1. What is Futures Trading?
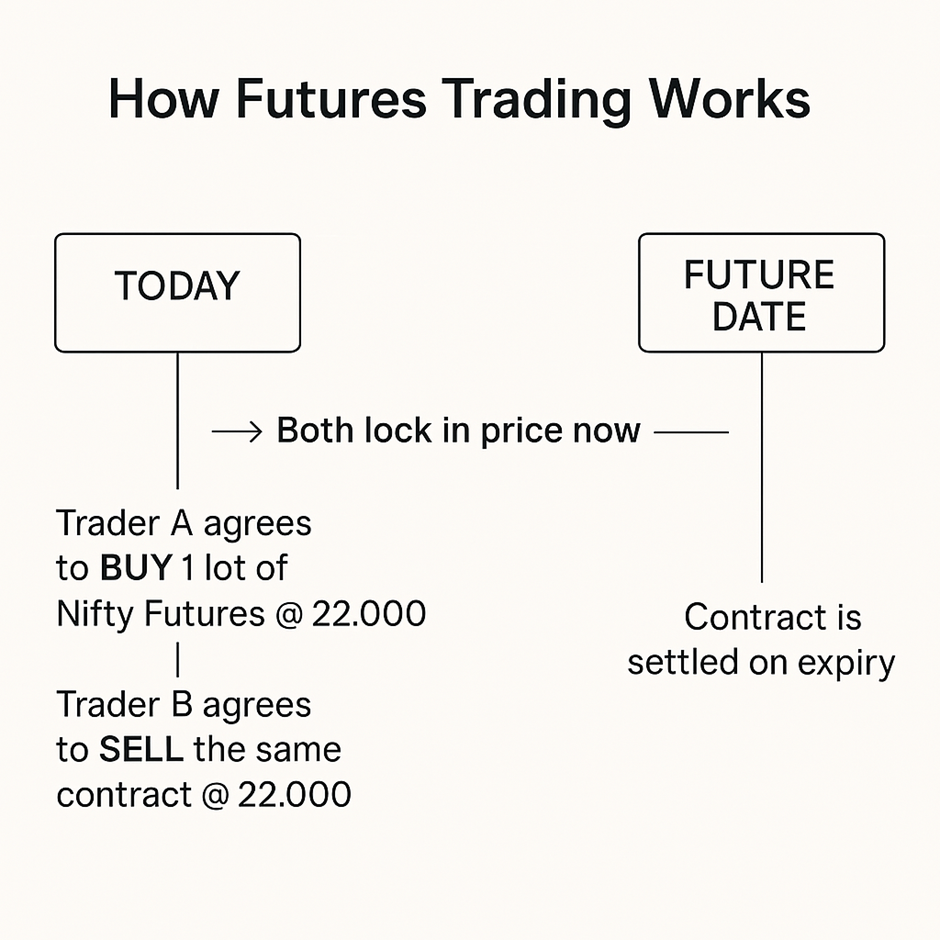
Futures trading is a type of derivatives trading where two parties agree to buy or sell an asset at a specific price on a future date. Rather than trading the asset itself (like stocks), traders buy and sell contracts based on the asset’s expected price movement.
These contracts are standardized and traded on regulated exchanges, such as the NSE (National Stock Exchange) or MCX (Multi Commodity Exchange) in India.
Why is it Called “Futures”?
Because the actual transaction (delivery or settlement) is scheduled for a future date, even though the price is agreed upon today.
Visual Overview:
Key Characteristics of Futures Trading
| Feature | Explanation |
|---|---|
Common Use Cases
- Speculation: Traders bet on the direction of prices and try to profit from short-term movements.
- Hedging: Investors or businesses use futures to protect against price fluctuations in stocks, commodities, or currencies.
- Arbitrage: Traders exploit price differences between the spot market and the futures market for risk-free profits.
Example
Imagine Nifty 50 is currently at 22,000.
A trader believes it will go up in the next 30 days.
- They buy 1 lot of Nifty Futures at 22,000.
- If Nifty moves to 22,500 before expiry:
- The trader squares off the position at 22,500
- Profit = (22,500 – 22,000) × lot size (50) = ₹25,000

Key Takeaways
- Futures trading is about predicting future price movements and trading contracts accordingly.
- It offers leverage, flexibility, and both long and short opportunities.
- Widely used by traders, investors, hedgers, and businesses.
- Understanding its structure is essential before moving into strategies and risks.