Chemical Sector Research Report
The chemical sector is a mainstay for several downstream industries.
chemical sector Overview:
-
The First efforts to manufacture chemicals indigenous in India were undertaken by Archarya Prafulla Chandra Ray in 1901, with the establishment of Bengal Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals works Limited (now known as BCPL) in Kolkata.
-
It was the first company to manufacture quality chemicals, drugs, pharmaceuticals, and home products in India.
-
Shalimar Paint color & Varnish Company (now known as Shalimar Paints) was the first company to start large-scale paint manufacturing in Howrah, West Bengal.
-
The chemical industry is a knowledge-intensive as well as capital-intensive sector.
-
It is the integral constituent of the growing Indian industry.
-
It includes basic chemicals, petrochemicals, fertilizers, paints, varnishes, gases, soaps, perfumes, toiletry, and pharmaceuticals.
-
The diversification within the chemical industry is large and covers more than eighty thousand commercial products.
-
The sector is the mainstay of industrial and agriculture development in the country and provides building blocks for several downstream industries such as textiles, papers, varnishes, soaps, detergents, pharmaceuticals, etc.
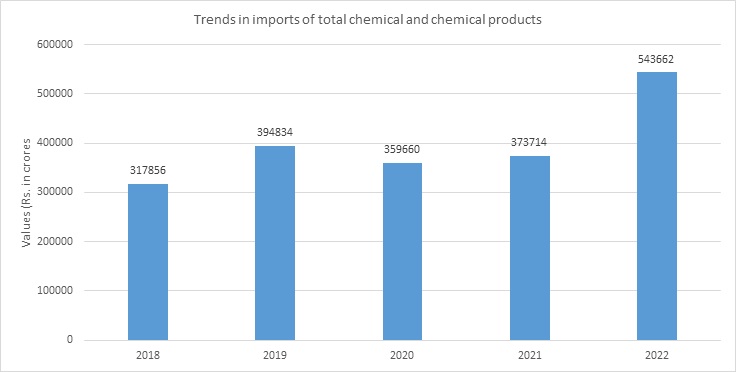
About Indian Chemical Industry
-
India is the 6th largest producer of chemicals in the world and the 3rd largest in Asia.
-
India is the 4th largest producer of agrochemicals in the world and manufactures more than 50% of technical-grade pesticides.
-
The chemicals and petrochemicals industry are expected to reach $300 billion by 2025.
-
Exports of Chemicals & Petrochemicals products contributed 11.9% of total exports in 2021-22.
-
India leads in Dyes production and contributes 16%-18% to the world’s Dyestuffs exports. India Dye is exported to more than 90 countries.
-
The quantum of production of major petrochemicals increased to 405.50 lakh tons during 2021-22 (up to February 2022) compared to 381.07 lakh tons during the corresponding period, recording an increase of 7.2% with the major rise in all sub-sectors.
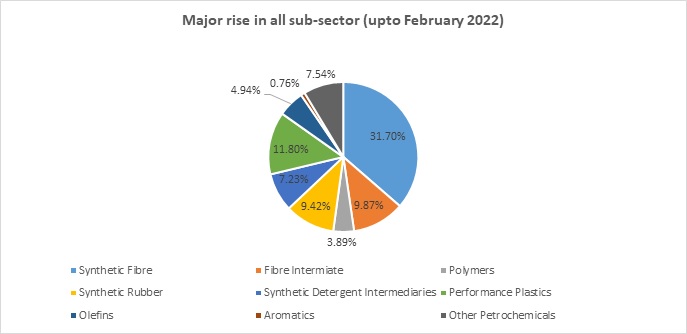
-
The Average Index of Industrial Production of Manufacturing of chemicals and chemical products in the FY 2021-22 is 120.7 and has grown by 4.1%.
-
The Agrochemicals market in India is expected to grow at an 8% CAGR reaching $4.7 billion by FY 2025.
-
The specialty chemicals constitute 22% of India's total chemicals and petrochemicals.
-
The quantum of production of major chemicals increases to 115.82 lakhs tones during 2021-22 (up to February 2022) compared to 101.52 lakh tones during the corresponding period, recording an increase of 14.09% with the major rise in all sub-sectors.
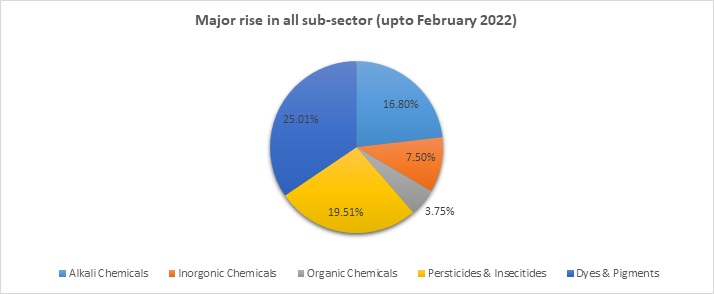
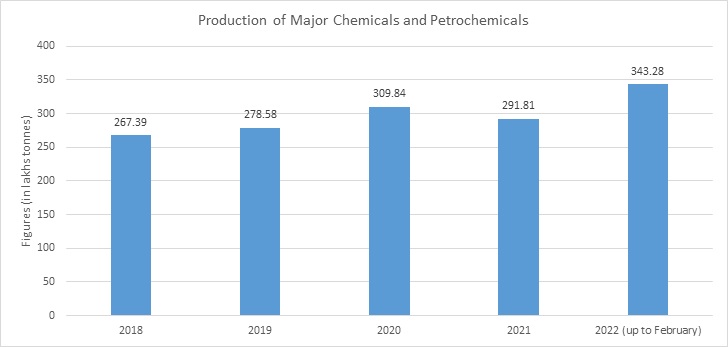
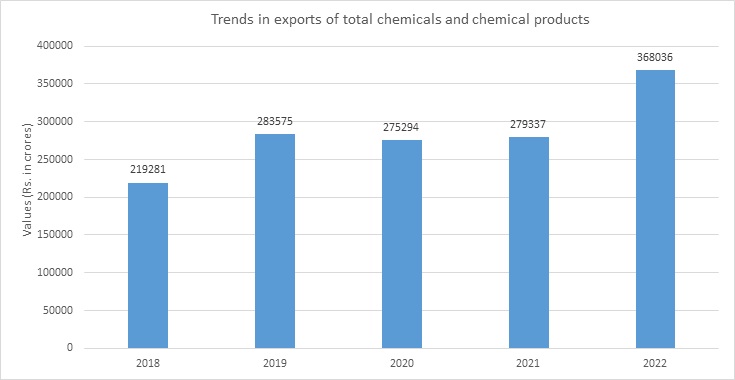
Product Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
-
Launched and approved in 2021 at a budgetary layout of ₹18,100 crores over 5 years.
-
Under the scheme, the government seeks to boost local manufacturing of advanced chemistry cells to bring down the prices of batteries in the country, which will also reduce the cost of electric vehicles.
-
The beneficiary firm was free to choose suitably advanced technology, machinery, raw material, and other intermediate goods for setting up a cell manufacturing facility to cater to any application.
-
A total of four companies were selected for the PLI scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage. This includes Reliance New Energy Solar limited, Ola Electric Mobility Private Limited, Hyundai Global Motors Company Limited, and Rajesh Exports Limited.
Union Budget FY 2022-23:
-
The total budget allocation for FY 2022-23 towards the Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals is ₹209 crore.
-
The total budget allocation for FY 2022-23 towards the Department of Fertilizers is ₹1,05,262.23 crore.
Government Initiative (Sector Policy):
-
Petroleum, Chemicals, and Petrochemicals Investment Regions (PCPIRs):
-
The Government of India has conceptualized PCPIRs as clusters that provide investors with transparent and investment-friendly policy and facility regimes.
-
PCPIRs have a high-class infrastructure and provide a competitive environment conducive to setting up a business.
-
The minimum processing area for the PCPIR will be about 40% of the total designated area, i.e., around 100 sq. km.
-
The Ministry of Chemicals & Petrochemicals has set up four PCPIRs in Dahej, Vishakhapatnam-Kakinada (Andhra Pradesh), Paradeep (Odisha), and Cuddalore & Nagapattinam (Tamil Nadu).
-
-
Plastic Parks:
-
The Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals has formulated the Scheme for setting up Plastic Parks with the objective of synergizing and consolidating the various units of the Indian Plastic Industry.
-
The Government of India will provide grant funding up to 50% of the project cost subject to a ceiling of ₹40 crores. The remaining project cost is funded by the Government or State Industrial Development Corporation.
-
Key Growth Drivers of the Chemicals and Petrochemicals (PCR) Industry:
-
Increasing middle class and working population:
-
By 2025, India’s working population is expected to increase by 33% to reach 1.14 million, along with tripled income level.
-
-
Increasing adoption of specialty products:
-
Increasing awareness of health and hygiene has resulted in the growing adoption of nutraceutical ingredients & personal home care ingredients.
-
The demand for engineering plastic and high-performance materials is increasing with rapid urbanization and industrialization led by the growth in automotive, electronics, consumer goods, construction, and other sectors.
-
-
Increasing focus on R&D:
-
Chemical companies are investing in R&D activities to develop their niche in the market.
-
-
Energy Efficiency:
-
Continued energy efficiency measures are leading to an increase in demand for plastic insulation polystyrene & polyurethanes, low thermal conductivity, and light-weight polycarbonates.
-
Opportunities for PCR Industry:
-
The structure of China’s chemical industry is changing due to the stricter environmental norms, tighter financing, and consolidation. These could cause uncertainty for international players that source chemicals from China. That could create opportunities for India’s chemical companies in certain value chains and segments.
-
Several global oil and gas majors are turning their sights on downstream chemical opportunities. This may increase the focus on petrochemicals in India and higher challenges and boost self-sufficiency.
-
Industry-wide, there seems to be a move toward prioritization of core businesses and consolidation on a great scale, often through big-ticket mergers and acquisitions. For players like India, the scale will matter even more, as it could fortify their competitive advantage.
-
Digital technology has established itself as a lever to enhance efficiency and productivity. Indian companies could also tap into this opportunity to expand their profit margins.
-
Ramping up the exports in select areas, such as specialty chemicals, to obtain a larger share of global value.
Challenges for PCR Industry:
-
The raw materials required in the organic and inorganic chemical industry, which even spans the specialty chemical industry, are often inaccessible and unavailable in the market in the required quantities. The primary materials like naphtha and natural gas are very high-priced in the Indian market compared to the Middle Eastern States, China, and other South-Eastern Countries.
-
Infrastructural complications like the absence of adequate facilities of ports, poor connectivity of pipelines, insufficient power supply, an abnormal condition of the railway system, and erratic nature of the transport system make it challenging for the chemical manufacturers to obtain raw materials from vendors across the country
-
Chemical manufacturers are facing growing problems in the documentation of product quality and compliance with various procedures. These issues are generally contributed by multi-level regulations imposed by the governments, requirements posed by the end-user market, as well as specific needs and necessities of the customers.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Adoption by Chemical Companies:
-
Several companies in the industry are taking significant strides toward improvement by employing innovative technologies to cut down emissions, kicking off decarbonization efforts, and enabling other sectors to become more sustainable.
-
As the key players in the manufacturing value chain, chemical companies gain an advantage through early preparation to comply with more stringent ESG standards. ESG-related ratings and frameworks increasingly play a role in shaping their innovation portfolios.
-
Though technologically feasible, full ESG compliance in all dimensions will cost at cost. Across the globe, governments provide strong financial support at national and multinational levels to assist the industry in its ESG transformations.
Alternative Fuels:
-
India has been pushing for alternate fuels such as ethanol and methanol to improve its energy efficiency.
-
India meets 85% of its crude oil requirement, 53% of its natural gas, and 25% of its coal requirement through imports.
-
Methanol is an alternate fuel blended with gasoline in the transport sector. It can be used to produce many downstream chemical and petrochemical products such as DME, Olefins, Acetic acid, etc.
-
Post the ‘Green Hydrogen Policy’ announced in February this year, the Union government has declared its plans to initiate the green hydrogen mission.
-
The announcement included the listing of sectors expected to incorporate the use of green hydrogen. Cheaper renewable power has also been assured, with the fee waivers being announced for projects commissioned before June 2025, as well as others, to aid in the transition to achieving net-zero.
Recent Scenarios:
-
The Russia-Ukraine war has severely disrupted the global economy.
-
The Indian economy has just started to recover from the covid-19 shocks, but the Russia-Ukraine war pushed the economy back.
-
India, deficient in oil and natural gas, finds it difficult to cope with rising prices.
-
Rising crude oil prices and natural gas prices will severely impact inflation, economic progress, and market development.
-
On 8th June 2022, RBI raised the interest rate by 50 basis points to a two-year high of 4.9%.
-
It also revised the inflation projection to 6.7%.
-
CRR remains unchanged at 4.50%.
Conclusion:
-
The profitability of companies could get impacted directly or indirectly due to the increase in the price of raw materials such as crude oil and natural gas in the short term.
-
Improving the lifestyle of people, adaptability of upgrade technology, various measures are taken by the government, increasing awareness of climate change, anti-pollution measures by China, and sector-specific skill programs will directly or indirectly benefit the chemical sector in the long run.
Disclaimer: This report is only for the information of our customer’s recommendations, opinions, or suggestions given with the understanding that readers acting on this information assume all risks involved. The information provided herein is not construed as an offer to buy or sell securities of any kind.
Post a Comment
|
DISCLAIMER |
This report is only for the information of our customers. Recommendations, opinions, or suggestions are given with the understanding that readers acting on this information assume all risks involved. The information provided herein is not to be construed as an offer to buy or sell securities of any kind. ATS and/or its group companies do not as assume any responsibility or liability resulting from the use of such information.





